The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
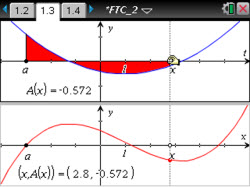
Students make visual connections between a function and its definite integral.
- Students will be able to identify the graphical connections between a function and its accumulation function.
- For a given function, students will recognize the accumulation function as an antiderivative of the original function.
- Students will be able to apply and explain the second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
- Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. (CCSS Mathematical Practice)
- Look for and make use of structure. (CCSS Mathematical Practice)
- accumulation function
- definite integral
- antiderivative
The intent of this lesson is to help students make visual connections between a function and its definite integral.
- Students will use the accumulation function with a fixed starting point to find definite integrals of a function over different intervals.
- Students will observe that the accumulation function is an antiderivative of the original function.
- Students will apply the antiderivative property of the accumulation function in combination with their use of the accumulation function to determine a definite integral.
- The lesson concludes with students stating and applying an informal statement of the second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
- This lesson is designed to follow the lesson The First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
Vernier EasyData,Vernier EasyLink and Vernier EasyTemp are registered trademarks of Vernier Science Education.

