Conditional Probability
Conditional Probability
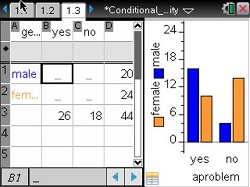
This lesson involves thinking about probability when additional information is given.
- Students will identify the difference between the probability of an outcome and the conditional probability of an outcome.
- Students will answer probability questions using information presented in a table and in a graph.
- conditional probability
- probability
- two-way table
This lesson involves thinking about probability when additional information is given.
As a result, students will:
- Investigate probability questions using tabular and graphical information.
- Explain why a two-way table with two rows and two columns with fixed row and column totals needs only one input to determine the others.
- Answer questions about the probability of an outcome using data from a two-way table.
- Use bar graphs separated according to categories to answer probabilities and connect these graphs to information of the form P(A|B).
- Choose between information presented as the probability of A given B and the probability of B given A (A|B and B|A) to answer specific probability questions.
Vernier EasyData,Vernier EasyLink and Vernier EasyTemp are registered trademarks of Vernier Science Education.

