DC Circuits
DC Circuits
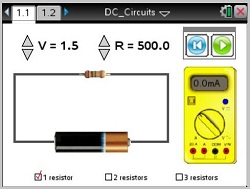
In this lesson, students explore an animation of particle flow in a battery.
- Students will explore an animation of particle flow in a battery.
- Students will vary the electron flow in a DC circuit with a battery of varying voltages and one, two, and three resistors.
- Students will observe changes in current (milliamps) with varying voltage and resistance.
- Students will describe a direct current both qualitatively and quantitatively.
- Students will use the formula Voltage = Current + Resistance (V=IR).
- Current
- DC Circuit
- Battery
- Resistance
- Amps and milliamps
- Resistors
- Ohms
- Voltage
- Volts
In this lesson, students will address the fact that a direct current flowing in a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference between its ends (V=I•R, where V is the potential difference, or voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance of the conductor).
As a result, students will:
- Explore the simulation of a DC Circuit.
- Develop the relationship V=I•R with a simulated DC Circuit.
- Calculate voltage, resistance, or current of several DC Circuits.
- Explore the formula beyond the simulation and use the simulation to verify.
- Discuss the rate and direction of the flow of electrons in the DC Circuit.
Vernier EasyData,Vernier EasyLink and Vernier EasyTemp are registered trademarks of Vernier Science Education.

