This lesson explores series and partial sums of infinite series. Series are used in many applications including integration, approximation, and the solution of differential equations. These applications arise in many disciplines, especially physics and chemistry.
Defining a Series
A series, which is not a list of terms like a sequence, is the sum of the terms in a sequence. If the series has a finite number of terms, it is a simple matter to find the sum of the series by adding the terms. However, when the series has an infinite number of terms the summation is more complicated and the series may or may not have a sum.
Defining Partial Sums
When working with series, it is often helpful to examine the partial sums that represent the sum of the first few terms.
Suppose an infinite sequence is defined by
![]() . The terms of the sequence are
. The terms of the sequence are
![]() .
.
The first four partial sums of the associated infinite series are shown below, where sk represents the sum of the first k terms of the sequence.
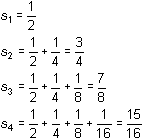
Each of the results shown above is a partial sum of the series
![]() which is associated with the sequence
which is associated with the sequence
![]() .
.
Defining the Sequence of Partial Sums of a Series
The partial sums of a series form a new sequence, which is denoted as {s1, s2, s3, s4,...}. For the series given above, the sequence of partial sums is
![]() .
.
If the sequence of partial sums for an infinite series converges to a limit L, then the sum of the series is said to be L and the series is convergent. Otherwise, the infinite series diverges.
Finding Partial Sums of Series
The TI-89 summation function and the Sequence Graphing mode are useful tools in understanding the sequence of partial sums and convergence of a series.
Using the Summation Function
Partial sums can be computed with the
![]() sum function and may be used to help explore whether or not the infinite series
sum function and may be used to help explore whether or not the infinite series
![]() converges. If it is convergent, the partial sums can also help estimate the sum of the series.
converges. If it is convergent, the partial sums can also help estimate the sum of the series.
|
|||
|
|
|||
- Perform NewProb
-
Open the Calc menu by pressing

"4:
![]() ( sum" is the fourth item in this menu.
( sum" is the fourth item in this menu.
-
Copy "
 (" to the Edit Line by highlighting "4:
(" to the Edit Line by highlighting "4:
 ( sum" and pressing
( sum" and pressing

Beginning with Zero
Explore the partial sums of the series
![]() . The first term in this series corresponds to
. The first term in this series corresponds to
k = 0, and that term is the first partial sum as well. The second partial sum is found by adding the first two terms, corresponding to k = 0 and k = 1. In general, the nth partial sum is found by adding the terms corresponding to k = 0, 1, ..., (n - 1).
-
Enter the command
 ((2^k + 5)/3^k, k , 0 , 4)
((2^k + 5)/3^k, k , 0 , 4)
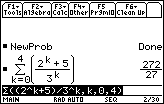
This result is called the fifth partial sum because the first five terms corresponding to k = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 were added.
-
Find a decimal approximation for this partial sum by pressing

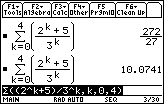
21.2.1 Approximate the tenth partial sum of the infinite series
![]() .
.
Click here for the answer.
Graphing the Sequence of Partial Sums
The graph of the sequence of partial sums for the infinite series
![]() can be created by defining the sequence of partial sums in the Y= Editor in Sequence Graph mode. You will need to enter the summation function from the catalog by pressing
can be created by defining the sequence of partial sums in the Y= Editor in Sequence Graph mode. You will need to enter the summation function from the catalog by pressing
![]()
![]() , scrolling down the list to
, scrolling down the list to
![]() ( sum and pressing
( sum and pressing
![]() . Alternatively, you could press
. Alternatively, you could press
![]()
![]() and scroll up to the summation function.
and scroll up to the summation function.
-
Define u1(n) =
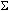 ((2^k+5)/3^k, k, 0, n) in the Y= Editor
((2^k+5)/3^k, k, 0, n) in the Y= Editor
Recall that n is the independent variable in Sequence Graphing mode.
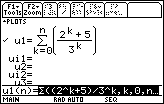
- Use the following window values:
| nmin = 0 | xmin = -1 | ymin = -1 |
| nmax = 10 | xmax = 11 | ymax = 15 |
| plotStrt = 1 | xscl = 1 | yscl = 1 |
| plotStep = 1 |
-
Graph the sequence of partial sums by pressing

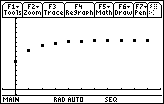
Each point of this graph represents a partial sum.
- Trace to the tenth partial sum (n = 9)
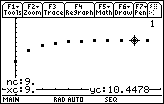
This should be the same value for the tenth partial sum that you computed earlier on the Home Screen.
21.2.2 The graph of the sequence of partial sums levels off. What does this imply?
Click here for the answer.
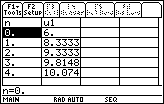
Creating a Table of Values for the Partial Sums
Make a table to show the partial sums.
-
Open the Table Setup dialog box by pressing

-
Set TblStart = 0 and
 tbl = 1 and save the values
tbl = 1 and save the values
-
Open the table by pressing
 [TABLE]
[TABLE]
Using the "Ask" Mode
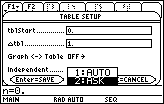
You can compute partial sums of your choosing by returning to the Table Setup dialog box and selecting the "ASK" mode.
-
Open the Table Setup dialog box by pressing

-
Open the submenu labeled "Independent" by moving the cursor to the line then pressing
- Highlight "2:ASK".
-
Select this mode and save the choices by pressing
 twice
twice
-
Clear the table by pressing

-
Enter 9 for n in the first row and press

- Move the cursor to the next row and enter 15 for n
- Move the cursor to the next row and enter 25 for n
- Move the cursor to the next row and enter 50 for n
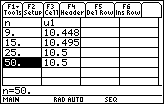
The table provides further evidence that the series converges.
|
|||
|
|
|||
Using the Ratio Test
The ratio test can confirm the convergence of this series.
Theorem (Ratio Test)
If
![]() for a series of positive terms, then the infinite series
for a series of positive terms, then the infinite series
![]() converges.
converges.
|
|||
|
|
|||
21.2.3 Define a function
![]() and evaluate
and evaluate
![]() .
.
Click here for the answer.
21.2.4 The ratio test showed that the series converges. To what value do you think the series converges?
Click here for the answer.