This lesson investigates finding analytical solutions to differential equations by using the TI-89's deSolve command and explores finding solutions to initial-value problems.
An equation containing a derivative such as y' = 2x, where y' denotes the derivative
![]() , is called a differential equation. Such equations occur often in real-world applications.
, is called a differential equation. Such equations occur often in real-world applications.
Finding Solutions to Differential Equations
A solution to a differential equation is a function that satisfies the differential equation and there may be more than one solution. Each of the functions shown below is a solution to the differential equation y' = 2x because each makes the differential equation true.
y1 = x2
y2 = x2 + 1
y3 = x2 – 3
These particular solutions, as well as all other solutions to the differential equation y' = 2x, can be described by the function
y = x2 + C
where C represents any real number. This family of functions is called the general solution to the differential equation.
Using the deSolve Command
The TI-89 deSolve command can be used to find general solutions to simple differential equations like y' = 2x and to more complicated differential equations as well.
Solve y' = 2x by following the procedure below.
- Go to the Home Screen and execute NewProb
-
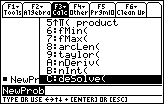
Open the Calc menu by pressing

- Scroll down the menu and highlight "C:deSolve(
-
Paste this command to the Edit Line by pressing

|
|||
|
|
|||
- Execute deSolve(y'=2x,x,y)
Note that
![]() is above
is above
![]() .
.

|
|||
|
|
|||
The solution may be verified by substituting the result into the original differential equation.
![]()
18.3.1 Use the deSolve command to find the general solution to the differential equation
y' = ex sin x
Click here for the answer.
|
|||
|
|
|||
18.3.2 Use deSolve to find the general solution to the differential equation
y' = y
Click here for the answer.
Solving Initial-Value Problems
Solve the differential equation y' = 2x with the condition that y(0) = 1, that is, y = 1 when x = 0. The condition y(0) = 1 is called an initial condition and a differential equation with an initial condition is called an initial-value problem.
Solve the initial-value problem y' = 2x and y(0) = 1.
- Execute NewProb
- Execute deSolve(y'=2x and y(0)=1,x,y)
Recall that "and " is found in the catalog.
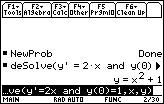
The solution to an initial-value problem is called a particular solution to the differential equation. The initial condition selects a particular solution from the family of general solutions.
18.3.3 Solve the initial-value problem y' = 2x and y(2) = 1.
Click here for the answer.
|
|||
|
|
|||
18.3.4 Solve the initial-value problem
![]() and y(1) = 3. Don't forget to insert a multiplication sign between y and ln(x).
and y(1) = 3. Don't forget to insert a multiplication sign between y and ln(x).
Click here for the answer.