Lesson 25.1 introduced polar coordinates and Lesson 25.2 investigated the graphs of polar equations. This lesson explores finding the area bounded by polar graphs.
Finding the Area Bounded by Polar Graphs
The area of the region between the origin and the curve r = f(
![]() ) for
) for
![]() is given by the definite integral
is given by the definite integral
![]()
The definite integral can be used to find the area of the region enclosed by the cardioid
r = 2(1 + cos
![]() ).
).
The entire graph of this function is plotted for
![]() , so the area is given by the definite integral
, so the area is given by the definite integral
![]()
Evaluate this integral on your TI-89.
-
Enter
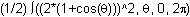
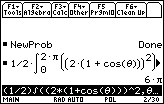
The area enclosed by the cardioid is 6
![]() square units.
square units.
25.3.1 Find the area enclosed by the curve r = 2 on the interval
![]() . Click here for the answer.
. Click here for the answer.
Finding the Area Between Two Polar Curves
The area bounded by two polar curves
![]() is given by
is given by
![]()
The definite integral can be used to find the area that lies inside the circle r = 1 and outside the cardioid r = 1 – cos
![]() .
.
First visualize the area by graphing both curves.
- Set r1 = 1
-
Set r2 = 1 – cos(
 )
)
-
Use a [0,2
 ] x [-4,4] x [-2,2] viewing window
] x [-4,4] x [-2,2] viewing window
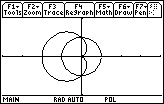
The area inside the circle and outside the cardioid lies in the first and fourth quadrants.
To find the area between the curves you need to know the points of intersection of the curves.
- Return to the Home Screen
-
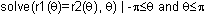
The symbol
![]() is entered by pressing
is entered by pressing
![]()
![]() .
.
|
|||
|
|
|||
The definite integral that gives the area is
![]()
-
Enter
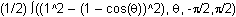
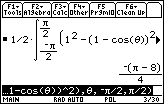
The area is
![]() square units.
square units.
25.3.2 Find the area of the region inside the circle r = 3 sin
![]() and outside the cardoid r = 1 + sin
and outside the cardoid r = 1 + sin
![]() . Click here for the answer.
. Click here for the answer.