In previous modules you used the definite integral to find the area bounded by a function and the x-axis. In each case the graph of the function was above the x-axis. In this lesson you will see what happens when the function dips below the x-axis. You will also investigate the concept of the definite integral as a net-area function.
All the curves explored in Module 18 were above the x-axis. The following investigates a definite integral when part of the curve is below the x-axis.
-
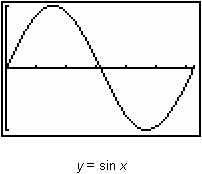
Graph y = sinx in a [0, 2
 , 1] x [-1, 1, 1] window.
, 1] x [-1, 1, 1] window.
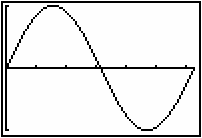
-
Evaluate the integral
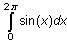 by using the integral key.
by using the integral key.
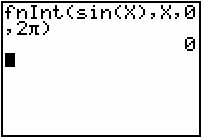
How can the result be zero? The area bounded by y = sin x and the x-axis certainly is not zero. To help answer this question, break the interval of integration into two subintervals that represent the areas above and below the x-axis: [0,
![]() ] and [
] and [
![]() , 2
, 2
![]() ].
].
-
Evaluate
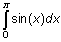 and
and
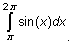 .
.
Finding Positive and Negative Integrals
Review the graph of y = sin x and the values of the definite integrals
![]() and
and
![]() .
.
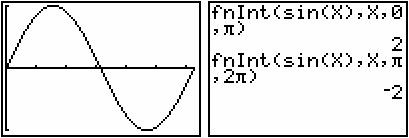
The graph from 0 to
![]() is above the x-axis and the corresponding definite integral is positive.
is above the x-axis and the corresponding definite integral is positive.
The graph from
![]() to 2
to 2
![]() is below the x-axis and the corresponding definite integral is negative.
is below the x-axis and the corresponding definite integral is negative.
Finding Net Area
The definite integral
![]() represents the value of the net area, or the area above the x-axis minus the area below the x-axis. From the above, we know the area above the x-axis is 2 and the area below the x-axis is 2. The net area between the curve y = sinx and the x-axis on this interval is therefore 2 minus 2, or zero.
represents the value of the net area, or the area above the x-axis minus the area below the x-axis. From the above, we know the area above the x-axis is 2 and the area below the x-axis is 2. The net area between the curve y = sinx and the x-axis on this interval is therefore 2 minus 2, or zero.
![]()
19.1.1 Use the definite integral feature
![]() in the CALC menu of the Graph screen to approximate the values of
in the CALC menu of the Graph screen to approximate the values of
![]()
Click here for the answer.
Visualizing
![]()
You can obtain the general shape of a corresponding net area function on the interval [0, 2
![]() ] by examining the graph of y = sinx.
] by examining the graph of y = sinx.
-
Refresh the graph of y = sin x by pressing

 .
.
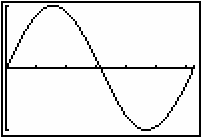
The following characteristics of the net area function
![]() can be determined from the graph of the curve y = sinx. Look at the graph while reading the tables below. Recall that the curve function is the derivative of the net area function, or in this case, F ' (x) = sin(x).
can be determined from the graph of the curve y = sinx. Look at the graph while reading the tables below. Recall that the curve function is the derivative of the net area function, or in this case, F ' (x) = sin(x).
| x-axis Interval | Curve Function | Area Function |
|
[0,
|
positive | increasing |
|
[
|
negative | decreasing |
|
|
increasing | concave upward |
|
|
decreasing | concave downward |
Furthermore, the x-values where maximums, minimums, and points of inflection occur can be identified by examining how the curve function is changing.
| x-value | Curve Function is Changing | Area Function |
|
x =
|
from positive to negative | local maximum |
|
|
from increasing to decreasing | point of inflection |
|
|
from decreasing to increasing | point of inflection |
Other characteristics of the net area function include:
- When x = 0, the net area is 0.
-
The net area on the interval [0,
 ] is 2 and the net area function begins to decrease at that point, so the maximum of the net area function is 2 when x =
] is 2 and the net area function begins to decrease at that point, so the maximum of the net area function is 2 when x =
 .
.
-
The net area on the interval [0, 2
 ] is 0, so the net area function is 0 when x = 2
] is 0, so the net area function is 0 when x = 2
 .
.
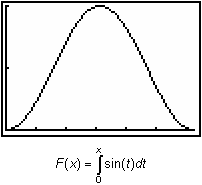
With these characteristics you can draw a graph of the net area function
![]() . Using the TI-83 we can graph F(x) and support the above results.
. Using the TI-83 we can graph F(x) and support the above results.
Graph F(x) by following the procedure below.
- Enter Y1 = fnInt(sin(T),T,0.X).
- Display the graph in a [0, 2
 , 1] x [0, 2, 1] window.
, 1] x [0, 2, 1] window.
|
|
Visualizing the general shape of the integral function
![]() is often very helpful.
is often very helpful.
Extending the Procedure to Other Curves
19.1.2 Graph the curve and find the net area bounded by y = x3 – 3x2 – x + 3 and the x-axis on the interval [0, 4].
Click here for the answer.
Visualizing
![]()
The characteristics of the net area function
![]() can be found by examining the graph of the curve function. The graph of the curve is shown below in a [0, 4, 1] x [ -5, 15, 1] window with a list of the net area function's characteristics.
can be found by examining the graph of the curve function. The graph of the curve is shown below in a [0, 4, 1] x [ -5, 15, 1] window with a list of the net area function's characteristics.
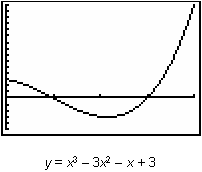
|
|
The graphs of the curve function and the net area function are shown below for comparison.
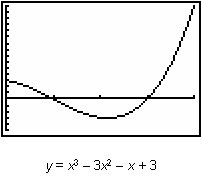
|
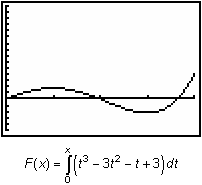
|
19.1.3 Sketch the graph of the net area function
![]() that corresponds to the following curve in the window [0, 4, 1] x [-2, 2, 1].
that corresponds to the following curve in the window [0, 4, 1] x [-2, 2, 1].
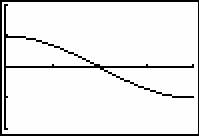
Click here for the answer.