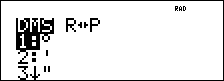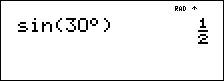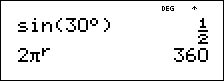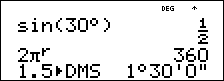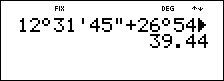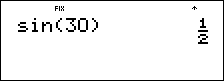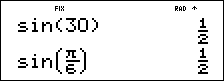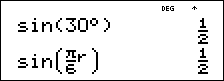% I
% I displays the choice of two submenus that enable you to specify the angle unit modifier as degrees (°), minutes ('), seconds ("); radian (r); gradian (g), or convert units using 4DMS. You can also convert between rectangular coordinate form (R) and polar coordinate form (P). (See Rectangular to Polar for more information.)
Choose an angle mode from the mode screen. You can choose from
Examples
|
|
p " < |
|
|
|
- > 30 % I |
|
|
|
4 E < |
|
|
|
p < |
|
|
|
- 2 g % I 4 < |
|
|
4
|
1.5 % I 6 < |
|
³ Problem
Two adjacent angles measure 12¡ 31¢ 45£ and 26¡ 54¢ 38£. respectively. Add the two angles and display the result in
|
- p $ $ " " " < p |
|
|
- 12 % I |
|
|
1 31 % I 2 45 % I 3 T 26 % I 1 54 % I 2 38 % I 3 < |
|
|
% I 6 < |
|
The result is 39 degrees, 26 minutes and 23 seconds.
³ Problem
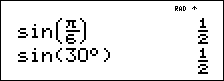
It is known that 30¡ = p / 6 radians. In the default mode, degrees, find the sine of 30¡. Then set the calculator to radian mode and calculate the sine of p / 6 radians.
Note: Press - to clear the screen between problems.
|
- > 30 E < |
|
|
p " < - > g q 6 " E < |
|
Retain radian mode on the calculator and calculate the sine of 30°. Change the calculator to degree mode and find the sine of p / 6 radians.
|
> 30 % I < E < |
|
|
p < - > g q 6 " % I E < |
|