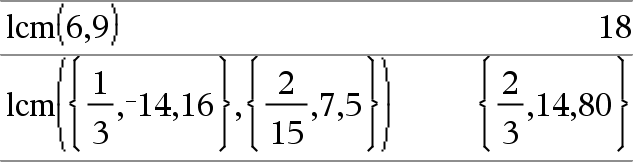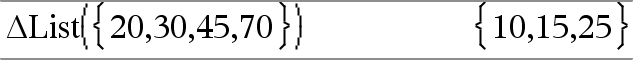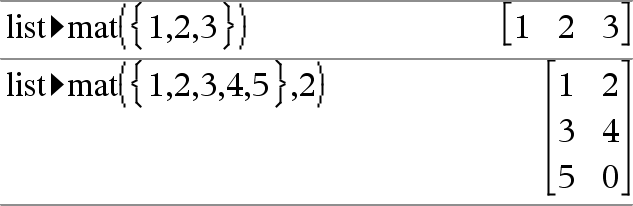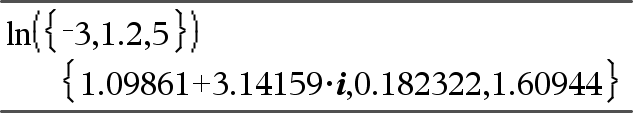|
Catalog > |
|
|
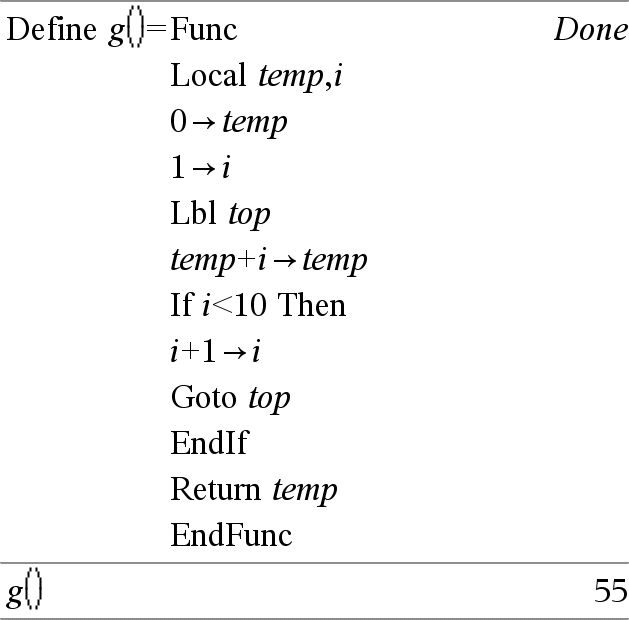
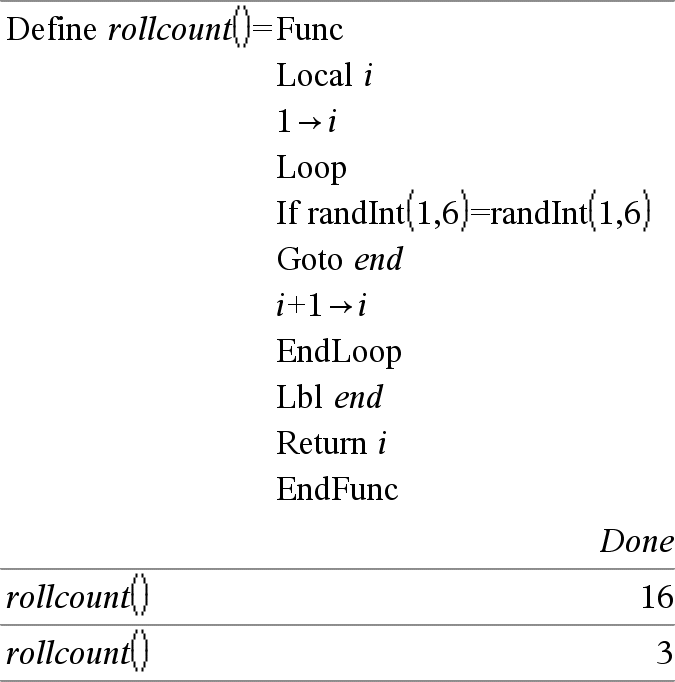
Lbl labelName Defines a label with the name labelName within a function. You can use a Goto labelName instruction to transfer control to the instruction immediately following the label. labelName must meet the same naming requirements as a variable name. Note for entering the example: For instructions on entering multi-line program and function definitions, refer to the Calculator section of your product guidebook. |
|
|
Catalog > |
|
|
lcm(Number1, Number2) ⇒ expression Returns the least common multiple of the two arguments. The lcm of two fractions is the lcm of their numerators divided by the gcd of their denominators. The lcm of fractional floating-point numbers is their product. For two lists or matrices, returns the least common multiples of the corresponding elements. |
|
|
Catalog > |
|
|
left(sourceString[, Num]) ⇒ string Returns the leftmost Num characters contained in character string sourceString. If you omit Num, returns all of sourceString. |
|
|
left(List1[, Num]) ⇒ list Returns the leftmost Num elements contained in List1. If you omit Num, returns all of List1. |
|
|
left(Comparison) ⇒ expression Returns the left-hand side of an equation or inequality. |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
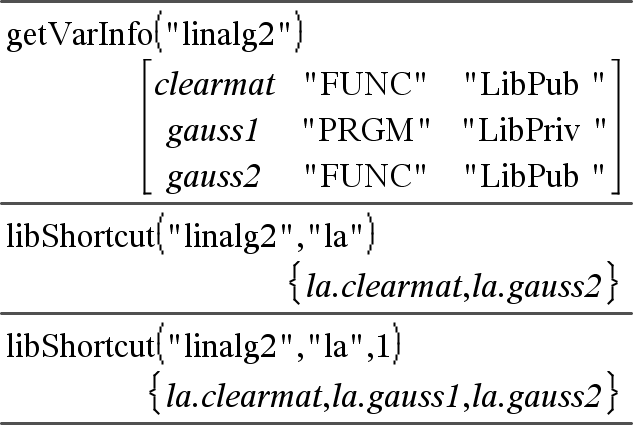
libShortcut(LibNameString, ShortcutNameString Creates a variable group in the current problem that contains references to all the objects in the specified library document libNameString. Also adds the group members to the Variables menu. You can then refer to each object using its ShortcutNameString. Set LibPrivFlag=0 to exclude private library objects (default) To copy a variable group, see CopyVar on here. |
This example assumes a properly stored and refreshed library document named linalg2 that contains objects defined as clearmat, gauss1, and gauss2.
|
|
Catalog > |
|
|
LinRegBx X,Y[,[Freq][,Category,Include]] Computes the linear regression y = a+b•x on lists X and Y with frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See here.) All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include. X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables. Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers ≥ 0. Category is a list of Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data items whose category code is included in this list are included in the calculation. For information on the effect of empty elements in a list, see “Empty (Void) Elements,” here. |
|
|
Output variable |
Description |
|
stat.RegEqn |
Regression Equation: a+b•x |
|
stat.a, stat.b |
Regression coefficients |
|
stat.r2 |
Coefficient of determination |
|
stat.r |
Correlation coefficient |
|
stat.Resid |
Residuals from the regression |
|
stat.XReg |
List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.YReg |
List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.FreqReg |
List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
LinRegMx X,Y[,[Freq][,Category,Include]] Computes the linear regression y = m•x+b on lists X and Y with frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See here.) All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include. X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables. Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers ≥ 0. Category is a list of Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data items whose category code is included in this list are included in the calculation. For information on the effect of empty elements in a list, see “Empty (Void) Elements,” here. |
|
|
Output variable |
Description |
|
stat.RegEqn |
Regression Equation: y = m•x+b |
|
stat.m, stat.b |
Regression coefficients |
|
stat.r2 |
Coefficient of determination |
|
stat.r |
Correlation coefficient |
|
stat.Resid |
Residuals from the regression |
|
stat.XReg |
List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.YReg |
List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.FreqReg |
List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
LinRegtIntervals X,Y[,F[,0[,CLev]]] For Slope. Computes a level C confidence interval for the slope. LinRegtIntervals X,Y[,F[,1,Xval[,CLev]]] For Response. Computes a predicted y-value, a level C prediction interval for a single observation, and a level C confidence interval for the mean response. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See here.) All the lists must have equal dimension. X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables. F is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in F specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers ≥ 0. For information on the effect of empty elements in a list, see “Empty (Void) Elements,” here. |
|
|
Output variable |
Description |
|
stat.RegEqn |
Regression Equation: a+b•x |
|
stat.a, stat.b |
Regression coefficients |
|
stat.df |
Degrees of freedom |
|
stat.r2 |
Coefficient of determination |
|
stat.r |
Correlation coefficient |
|
stat.Resid |
Residuals from the regression |
For Slope type only
|
Output variable |
Description |
|
[stat.CLower, stat.CUpper] |
Confidence interval for the slope |
|
stat.ME |
Confidence interval margin of error |
|
stat.SESlope |
Standard error of slope |
|
stat.s |
Standard error about the line |
For Response type only
|
Output variable |
Description |
|
[stat.CLower, stat.CUpper] |
Confidence interval for the mean response |
|
stat.ME |
Confidence interval margin of error |
|
stat.SE |
Standard error of mean response |
|
[stat.LowerPred, |
Prediction interval for a single observation |
|
stat.MEPred |
Prediction interval margin of error |
|
stat.SEPred |
Standard error for prediction |
|
stat.y |
a + b•XVal |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
LinRegtTest X,Y[,Freq[,Hypoth]] Computes a linear regression on the X and Y lists and a t test on the value of slope β and the correlation coefficient ρ for the equation y=α+βx. It tests the null hypothesis H0:β=0 (equivalently, ρ=0) against one of three alternative hypotheses. All the lists must have equal dimension. X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables. Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers ≥ 0. Hypoth is an optional value specifying one of three alternative hypotheses against which the null hypothesis (H0:β=ρ=0) will be tested. For Ha: β≠0 and ρ≠0 (default), set Hypoth=0 A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See here.) For information on the effect of empty elements in a list, see “Empty (Void) Elements,” here. |
|
|
Output variable |
Description |
|
stat.RegEqn |
Regression equation: a + b•x |
|
stat.t |
t-Statistic for significance test |
|
stat.PVal |
Smallest level of significance at which the null hypothesis can be rejected |
|
stat.df |
Degrees of freedom |
|
stat.a, stat.b |
Regression coefficients |
|
stat.s |
Standard error about the line |
|
stat.SESlope |
Standard error of slope |
|
stat.r2 |
Coefficient of determination |
|
stat.r |
Correlation coefficient |
|
stat.Resid |
Residuals from the regression |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
Returns a list of solutions for the variables Var1, Var2, ... The first argument must evaluate to a system of linear equations or a single linear equation. Otherwise, an argument error occurs. For example, evaluating linSolve(x=1 and x=2,x) produces an “Argument Error” result. |
|
|
Catalog > |
|
|
ΔList(List1) ⇒ list Note: You can insert this function from the keyboard by typing deltaList(...). Returns a list containing the differences between consecutive elements in List1. Each element of List1 is subtracted from the next element of List1. The resulting list is always one element shorter than the original List1. |
|
|
Catalog > |
|
|
list►mat(List [, elementsPerRow]) ⇒ matrix Returns a matrix filled row-by-row with the elements from List. elementsPerRow, if included, specifies the number of elements per row. Default is the number of elements in List (one row). If List does not fill the resulting matrix, zeros are added. Note: You can insert this function from the computer keyboard by typing list@>mat(...). |
|
|
/u keys |
|
|
Returns the natural logarithm of the argument. For a list, returns the natural logarithms of the elements. |
|
|
ln(squareMatrix1) ⇒ squareMatrix Returns the matrix natural logarithm of squareMatrix1. This is not the same as calculating the natural logarithm of each element. For information about the calculation method, refer to cos() on. squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains floating-point numbers. |
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular complex format:
To see the entire result, |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
LnReg X, Y[, [Freq] [, Category, Include]] Computes the logarithmic regression y = a+b•ln(x) on lists X and Y with frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See here.) All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include. X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables. Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers ≥ 0. Category is a list of Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data items whose category code is included in this list are included in the calculation. For information on the effect of empty elements in a list, see “Empty (Void) Elements,” here. |
|
|
Output variable |
Description |
|
stat.RegEqn |
Regression equation: a+b•ln(x) |
|
stat.a, stat.b |
Regression coefficients |
|
stat.r2 |
Coefficient of linear determination for transformed data |
|
stat.r |
Correlation coefficient for transformed data (ln(x), y) |
|
stat.Resid |
Residuals associated with the logarithmic model |
|
stat.ResidTrans |
Residuals associated with linear fit of transformed data |
|
stat.XReg |
List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.YReg |
List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.FreqReg |
List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
Local Var1[, Var2] [, Var3] ... Declares the specified vars as local variables. Those variables exist only during evaluation of a function and are deleted when the function finishes execution. Note: Local variables save memory because they only exist temporarily. Also, they do not disturb any existing global variable values. Local variables must be used for For loops and for temporarily saving values in a multi-line function since modifications on global variables are not allowed in a function. Note for entering the example: For instructions on entering multi-line program and function definitions, refer to the Calculator section of your product guidebook. |
|
|
Catalog > |
|
|
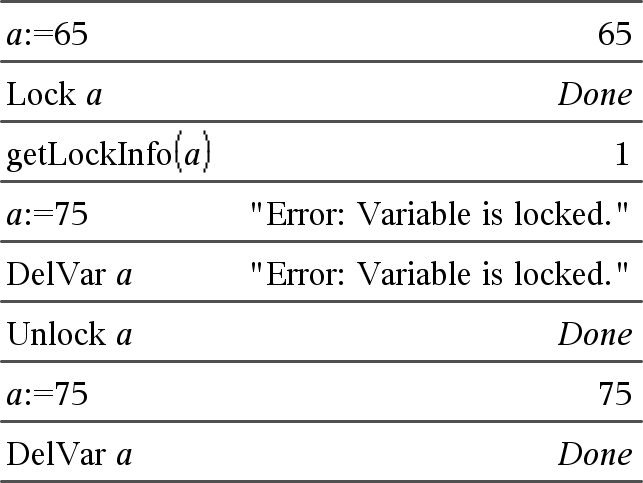
Locks the specified variables or variable group. Locked variables cannot be modified or deleted. You cannot lock or unlock the system variable Ans, and you cannot lock the system variable groups stat. or tvm. Note: The Lock command clears the Undo/Redo history when applied to unlocked variables. |
|
|
/s keys |
|
|
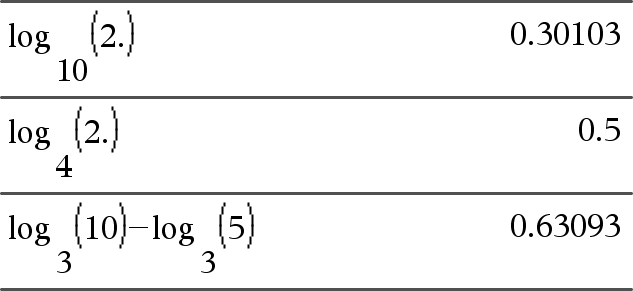
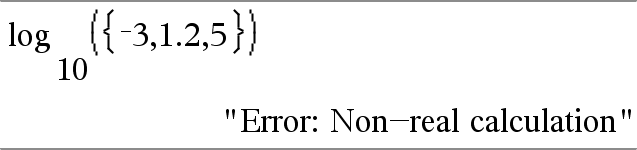
Returns the base-Value2 logarithm of the first argument. Note: See also Log template, here. For a list, returns the base-Value2 logarithm of the elements. If the second argument is omitted, 10 is used as the base. |
|
|
Returns the matrix base-Value logarithm of squareMatrix1. This is not the same as calculating the base-Value logarithm of each element. For information about the calculation method, refer to cos(). squareMatrix1 must be diagonalizable. The result always contains floating-point numbers. If the base argument is omitted, 10 is used as base. |
In Radian angle mode and Rectangular complex format:
To see the entire result, |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
Logistic X, Y[, [Freq] [, Category, Include]] Computes the logistic regression y = (c/(1+a•e-bx)) on lists X and Y with frequency Freq. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See here.) All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include. X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables. Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers ≥ 0. Category is a list of Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data items whose category code is included in this list are included in the calculation. For information on the effect of empty elements in a list, see “Empty (Void) Elements,” here. |
|
|
Output variable |
Description |
|
stat.RegEqn |
Regression equation: c/(1+a•e-bx) |
|
stat.a, stat.b, stat.c |
Regression coefficients |
|
stat.Resid |
Residuals from the regression |
|
stat.XReg |
List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.YReg |
List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.FreqReg |
List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
LogisticD X, Y [, [Iterations] , [Freq] [, Category, Include] ] Computes the logistic regression y = (c/(1+a•e-bx)+d) on lists X and Y with frequency Freq, using a specified number of Iterations. A summary of results is stored in the stat.results variable. (See here.) All the lists must have equal dimension except for Include. X and Y are lists of independent and dependent variables. Freq is an optional list of frequency values. Each element in Freq specifies the frequency of occurrence for each corresponding X and Y data point. The default value is 1. All elements must be integers ≥ 0. Category is a list of Include is a list of one or more of the category codes. Only those data items whose category code is included in this list are included in the calculation. For information on the effect of empty elements in a list, see “Empty (Void) Elements,” here. |
|
|
Output variable |
Description |
|
stat.RegEqn |
Regression equation: c/(1+a•e-bx)+d) |
|
stat.a, stat.b, stat.c, stat.d |
Regression coefficients |
|
stat.Resid |
Residuals from the regression |
|
stat.XReg |
List of data points in the modified X List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.YReg |
List of data points in the modified Y List actually used in the regression based on restrictions of Freq, Category List, and Include Categories |
|
stat.FreqReg |
List of frequencies corresponding to stat.XReg and stat.YReg |
|
Catalog > |
|
|
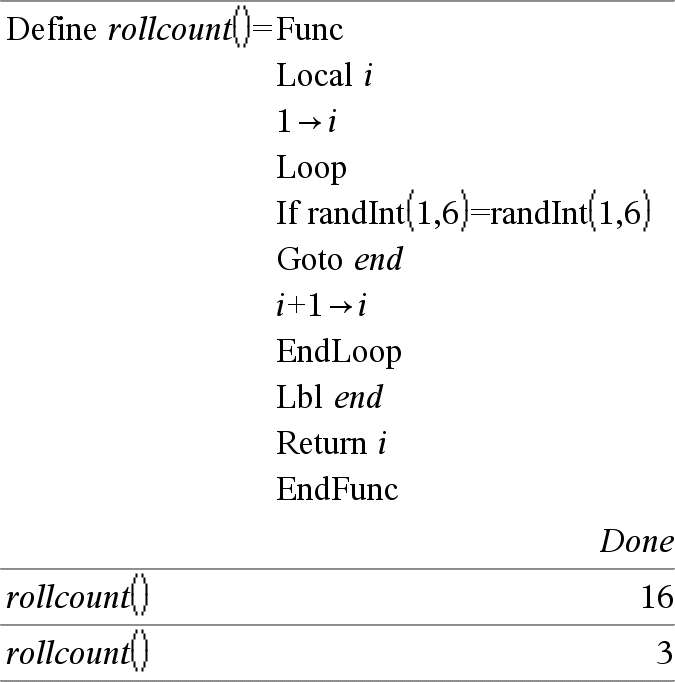
Loop Repeatedly executes the statements in Block. Note that the loop will be executed endlessly, unless a Goto or Exit instruction is executed within Block. Block is a sequence of statements separated with the “:” character. Note for entering the example: For instructions on entering multi-line program and function definitions, refer to the Calculator section of your product guidebook. |
|
|
Catalog > |
|||||||
|
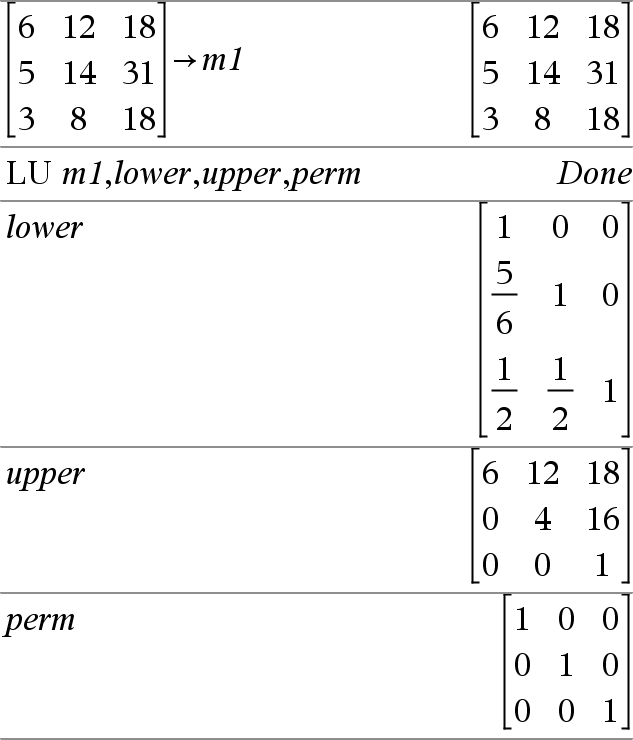
LU Matrix, lMatrix, uMatrix, pMatrix[,Tol] Calculates the Doolittle LU (lower-upper) decomposition of a real or complex matrix. The lower triangular matrix is stored in lMatrix, the upper triangular matrix in uMatrix, and the permutation matrix (which describes the row swaps done during the calculation) in pMatrix. lMatrix•uMatrix = pMatrix•matrix Optionally, any matrix element is treated as zero if its absolute value is less than Tol. This tolerance is used only if the matrix has floating-point entries and does not contain any symbolic variables that have not been assigned a value. Otherwise, Tol is ignored.
The LU factorization algorithm uses partial pivoting with row interchanges. |
|