Polar coordinates are an alternative way of identifying points in a plane. They are useful in many applications. For certain types of regions and curves, working in polar coordinates is much easier than working with (x, y) coordinates. Polar coordinates will be explored in this lesson and you will learn how to convert points given in rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates and vice-versa.
Defining Polar Coordinates
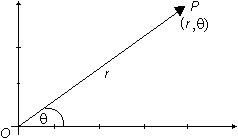
When assigning rectangular coordinates (x, y) to a point P in the plane, x is the horizontal distance and y is the vertical distance from the origin O to the point P.
If polar coordinates (r,
![]() ) are used instead, r is the directed distance from the origin to the point P and
) are used instead, r is the directed distance from the origin to the point P and
![]() is the directed angle from the positive x-axis to ray OP.
is the directed angle from the positive x-axis to ray OP.
Recall that there are an infinite number of angles that are coterminal with
![]() . Because any one of these angles can be used, there are infinitely many possible polar coordinates for each point in the plane.
. Because any one of these angles can be used, there are infinitely many possible polar coordinates for each point in the plane.
Converting Rectangular Coordinates to Polar Coordinates
The TI-83 has features that convert coordinates from rectangular to polar and vice-versa.
Suppose you wish to find a value of r for the rectangular point (3, 2).
- Select Radian in the Mode menu.
-
Open the Angle menu by pressing
 [ANGLE]. [ANGLE] is above
[ANGLE]. [ANGLE] is above
 .
.
-
Highlight
 (.
(.

This item returns the value of the r polar coordinate for a point given in rectangular coordinates.
-
Paste
 to the Home screen.
to the Home screen.
-
Complete the command
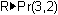 and press
and press
 .
.
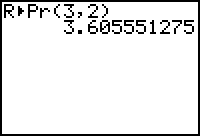
The distance from the origin O to the point (3, 2) is about 3.6056, so the polar coordinate r is about 3.6056.
A value of
![]() for this point may be found using a similar procedure.
for this point may be found using a similar procedure.
-
Open the Angle menu and highlight
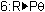 (.
(.

-
Press
 to paste this command to the Home screen.
to paste this command to the Home screen.
-
Complete the command
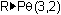 and press
and press
 .
.

The rectangular point (3, 2) is represented as approximately (3.61, 0.588) in polar coordinates. Because the calculator is in Radian mode, the angle measurement is given in radians.
27.1.1 If (r,
![]() ) are polar coordinates for a point P, what are the other possible polar coordinates for P? Click here for the answer.
) are polar coordinates for a point P, what are the other possible polar coordinates for P? Click here for the answer.
Converting from Polar to Rectangular Coordinates
27.1.2 Use the
![]() and
and
![]() features in the Angle menu to find the x- and y-coordinates for the polar point
features in the Angle menu to find the x- and y-coordinates for the polar point
![]() . Click here for the answer.
. Click here for the answer.
Unlike polar coordinates, the rectangular coordinates for any given point in the plane are unique.