|
Catalogue > |
||||||||||
|
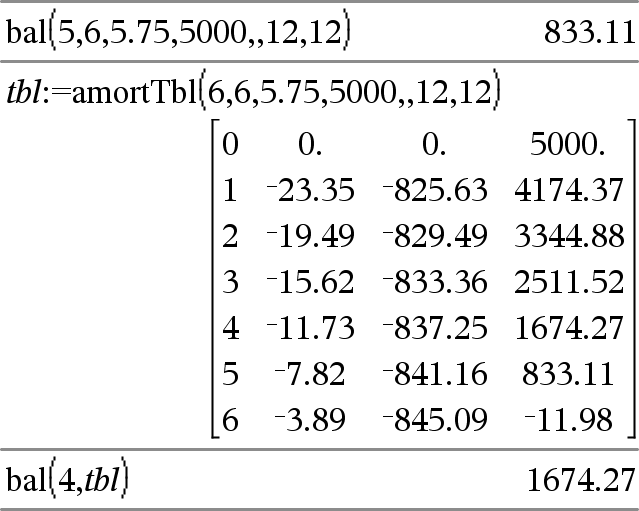
bal(NPmt,N,I,PV ,[Pmt], [FV], [PpY], [CpY], [PmtAt], [roundValue])Þvalue bal(NPmt,amortTable)Þvalue Amortisation function that calculates schedule balance after a specified payment. N, I, PV, Pmt, FV, PpY, CpY and PmtAt are described in the table of TVM arguments, here. NPmt specifies the payment number after which you want the data calculated. N, I, PV, Pmt, FV, PpY, CpY and PmtAt are described in the table of TVM arguments, here.
roundValue specifies the number of decimal places for rounding. Default=2. bal(NPmt,amortTable) calculates the balance after payment number NPmt, based on amortisation table amortTable. The amortTable argument must be a matrix in the form described under amortTbl(), here. Note: See also GInt() and GPrn(), here. |
|
|
Catalogue > |
|
|
Integer1 4Base2Þinteger Note: You can insert this operator from the computer keyboard by typing @>Base2. Converts Integer1 to a binary number. Binary or hexadecimal numbers always have a 0b or 0h prefix, respectively. Use a zero, not the letter O, followed by b or h. 0b binaryNumber 0h hexadecimalNumber |
|
|
A binary number can have up to 64 digits. A hexadecimal number can have up to 16. Without a prefix, Integer1 is treated as decimal (base 10). The result is displayed in binary, regardless of the Base mode. Negative numbers are displayed in “two's complement” form. For example, N1 is displayed as 0hFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF in Hex base mode 0b111...111 (64 1’s) in Binary base mode N263 is displayed as 0h8000000000000000 in Hex base mode 0b100...000 (63 zeroes) in Binary base mode If you enter a decimal integer that is outside the range of a signed, 64-bit binary form, a symmetric modulo operation is used to bring the value into the appropriate range. Consider the following examples of values outside the range. 263 becomes N263 and is displayed as 0h8000000000000000 in Hex base mode 0b100...000 (63 zeroes) in Binary base mode 264 becomes 0 and is displayed as 0h0 in Hex base mode 0b0 in Binary base mode N263 N 1 becomes 263 N 1 and is displayed as 0h7FFFFFFFFFFFFFFF in Hex base mode 0b111...111 (64 1’s) in Binary base mode |
|
|
Catalogue > |
|
|
Integer1 4Base10Þinteger Note: You can insert this operator from the computer keyboard by typing @>Base10. Converts Integer1 to a decimal (base 10) number. A binary or hexadecimal entry must always have a 0b or 0h prefix, respectively. 0b binaryNumber 0h hexadecimalNumber Zero, not the letter O, followed by b or h. A binary number can have up to 64 digits. A hexadecimal number can have up to 16. Without a prefix, Integer1 is treated as decimal. The result is displayed in decimal, regardless of the Base mode. |
|
|
Catalogue > |
|
|
Integer1 4Base16Þinteger Note: You can insert this operator from the computer keyboard by typing @>Base16. Converts Integer1 to a hexadecimal number. Binary or hexadecimal numbers always have a 0b or 0h prefix, respectively. 0b binaryNumber 0h hexadecimalNumber Zero, not the letter O, followed by b or h. A binary number can have up to 64 digits. A hexadecimal number can have up to 16. Without a prefix, Integer1 is treated as decimal (base 10). The result is displayed in hexadecimal, regardless of the Base mode. If you enter a decimal integer that is too large for a signed, 64-bit binary form, a symmetric modulo operation is used to bring the value into the appropriate range. For more information, see 4Base2, here. |
|
|
Catalogue > |
|
|
binomCdf(n,p)Þlist binomCdf(n,p,lowBound,upBound)Þnumber if lowBound and upBound are numbers, list if lowBound and upBound are lists binomCdf(n,p,upBound)for P(0{X{upBound)Þnumber if upBound is a number, list if upBound is a list Computes a cumulative probability for the discrete binomial distribution with n number of trials and probability p of success on each trial. For P(X { upBound), set lowBound=0 |
|
|
Catalogue > |
|
|
binomPdf(n,p)Þlist binomPdf(n,p,XVal)Þnumber if XVal is a number, list if XVal is a list Computes a probability for the discrete binomial distribution with n number of trials and probability p of success on each trial. |
|