Note: To avoid unexpected results when using this feature, make sure the document setting for "Real or Complex Format" is set to Real.
When you calculate the area between curves, each curve must be:
| • | A function with respect to x. |
- or -
| • | An equation in the form y=, including y= equations defined through a text box or a conic equation template. |
| 1. | From the Analyze Graph menu, select Bounded Area. |
If exactly two appropriate curves are available, they are selected automatically, and you can skip to step 3. Otherwise, you are prompted to select two curves.
| 2. | Click two curves to select them. – or – Click one curve and the x axis. |
You are prompted to set the lower and upper bounds.

| 3. | Click two points to define the bounds. Optionally, you can type numeric values. |
The area becomes shaded, and the area value is displayed. The value is always non-negative, regardless of the interval direction.
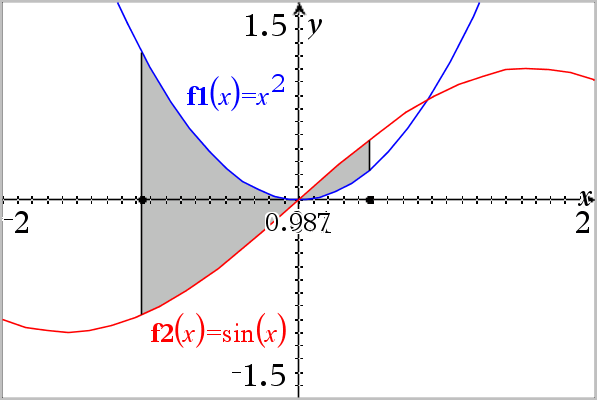
As you change the bounds or redefine the curves, the shading and the area value are updated .
| • | To change the lower or upper bound, drag it or type new coordinates for it. You cannot move a bound that resides on an intersection. However, the point moves automatically as you edit or manipulate the curves. |
| • | To redefine a curve, either manipulate it by dragging or edit its expression in the entry line. |
If an endpoint resided originally on an intersection, and the redefined functions no longer intersect, the shading and area value disappear. If you redefine the function(s) so that there is an intersection point, the shading and area value reappear.
| • | To delete or hide the shaded area, or to change its color and other attributes, display its context menu. |
| - | Windows®: Right-click the shaded area. |
| - | Mac®: Hold “ and click the shaded area. |
| - | Handheld: Move the pointer to the shaded area and press / x. |