% Q
q " <
% Q
0 " g " "
z X z ) "
<
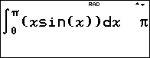
% Q pastes the numerical integral template from the keypad to calculate the numerical integral on a given interval with the default tolerance H is 1EM5.
|
% Q |
q " < % Q 0 " g " " z X z ) " < |
|
To change the default tolerance, H, and observe how the tolerance plays a role in the numerical solution, paste the numerical integral from the menu location, d MATH 8:fnInt(, where the numerical integral template will paste with the option to modify the tolerance as needed for an investigation of the numerical integral result.
|
d MATH 8:fnInt( with optional tolerance |
q < d 8 0 " 3 " z G 5 < |
|
In Classic mode or in classic edit lines, the fnInt( command will paste from the keypad or MATH menu.
Syntax: fnInt(expression,variable,upper,lower[,tolerance]) where tolerance is optional and the default H is 1EM5.
|
% Q or d MATH 8:fnInt( |
% Q z G 5 % . z % .0 % .3 ) < |
|
Find the area under the curve f(x) = Mx2+4 on the x intervals from M2 to 0 and then from 0 to 2. What do you notice about the results? What could you say about the graph of this function?
|
% Q M 2 " 0 " M z F T 4 " r |
|
|
< |
|
|
# # < % ! " 0 J " 2 |
|
|
< |
|
Notice that both areas are equal. Since this is a parabola with the vertex at (0,4) and zeros at (M2,0) and (2,0) you see that the symmetric areas are equal.