Example: Solving for Unequal Cash Flows
These examples show you how to enter and edit unequal cash-flow data to calculate:
| • | Net present value (NPV) |
| • | Internal rate of return (IRR) |
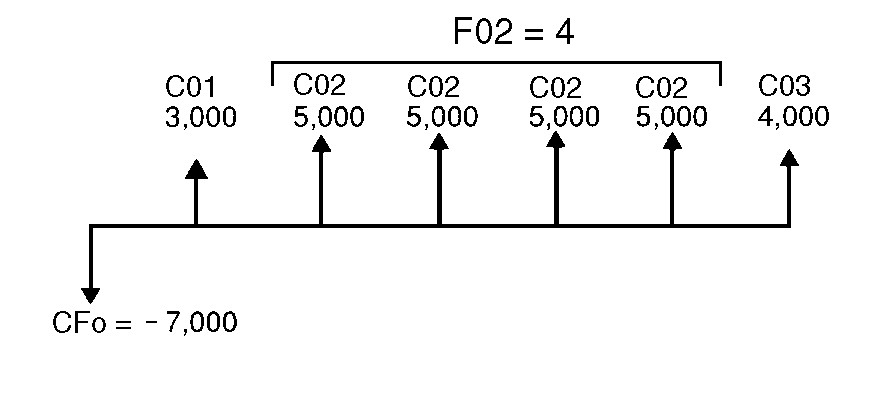
A company pays $7,000 for a new machine, plans a 20% annual return on the investment, and expects these annual cash flows over the next six years:
|
Year |
Cash Flow Number |
Cash Flow Estimate |
|
Purchase |
CFo |
-$7,000 |
|
1 |
C01 |
3,000 |
|
2–5 |
C02 |
5,000 each year |
|
6 |
C03 |
4,000 |
As the time line shows, the cash flows are a combination of equal and unequal values. As an outflow, the initial cash flow (CFo) appears as a negative value.
Entering Cash-Flow Data
|
To |
Press |
|
Display |
|
' |
CFo= |
0.00 |
|
|
Enter initial cash flow. |
7000 S! |
CFo= |
-7,000.001
|
|
Enter cash flow for first year. |
# 3000 ! |
C01= |
3,000.001 |
|
Enter cash flows for years two through five. |
# 5000 ! |
C02= |
5,000.001 4.001 |
|
Enter cash flow for sixth year. |
# 4000 ! |
C03= |
4,000.001 1.001 |
Editing Cash-Flow Data
After entering the cash-flow data, you learn that the $4,000 cash-flow value should occur in the second year instead of the sixth. To edit, delete the $4,000 value for year 6 and insert it for year 2.
|
To |
Press |
Display |
|
|
Move to third cash flow. |
" |
C03= |
4,000.001 |
|
Delete third cash flow. |
& W |
C03= |
0.00 |
|
Move to second cash flow. |
" " |
C02= |
5,000.001 |
|
Insert new second cash flow. |
& X 4000 ! # |
C02= |
4,000.001 |
|
Move to next cash flow to verify data. |
# |
C03= |
5,000.001 |
Computing NPV
Use an interest rate per period (I) of 20%.
|
To |
Press |
Display |
|
|
Access interest rate variable |
( |
I= |
0.00 |
|
Enter interest rate per period. |
20 ! |
I= |
20.001 |
|
Compute net present value. |
# C |
NPV= |
7,266.447
|
Answers: NPV is $7,266.44.
Computing IRR
|
To |
Press |
Display |
|
|
Access IRR. |
) |
IRR= |
0.00 |
|
Compute internal rate of return. |
C |
IRR= |
52.717 |
Answer: IRR is 52.71%.